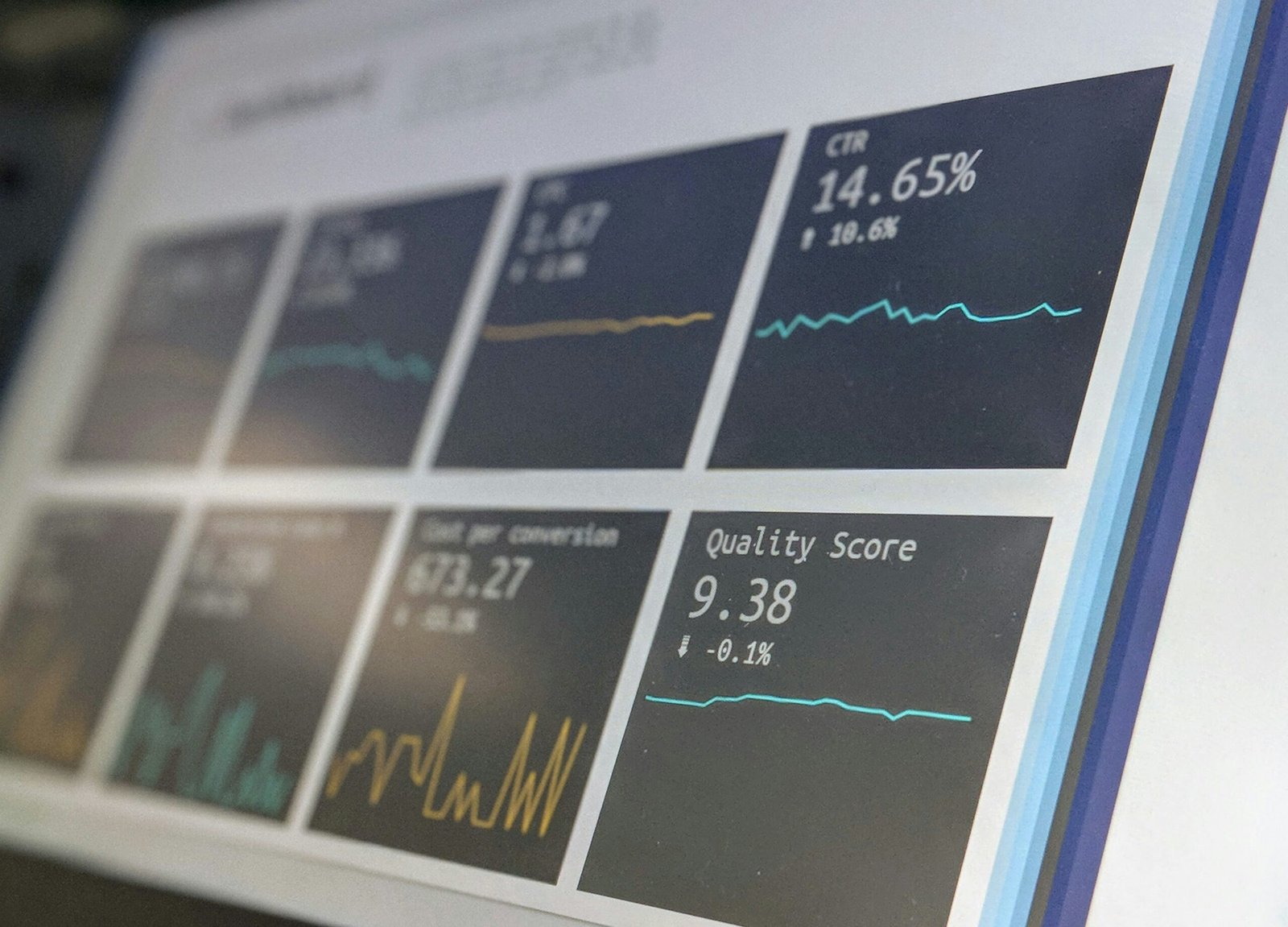
When it comes to investing in stocks, one term that you may often come across is “dividend.” In simple terms, a dividend is a distribution of profits made by a corporation to its shareholders. It is usually given in the form of cash payments or additional shares.
Why do companies pay dividends?
Companies pay dividends for several reasons. Firstly, it is a way for them to share their profits with shareholders. By distributing a portion of their earnings, companies reward their investors for their ownership in the business.
Secondly, dividends can attract investors. Many investors seek out stocks that offer regular dividend payments as it provides them with a steady income stream. This can be particularly appealing to retirees or individuals looking for passive income.
Lastly, paying dividends can be seen as a signal of financial health. Companies that consistently pay dividends demonstrate stability and confidence in their ability to generate profits.
Types of dividends
There are different types of dividends that companies may offer:
- Cash Dividends: This is the most common type of dividend, where shareholders receive cash payments directly into their brokerage accounts.
- Stock Dividends: Instead of cash, companies may choose to distribute additional shares to their shareholders. This increases the number of shares held by investors.
- Special Dividends: Occasionally, companies may issue special dividends, which are one-time payments made in addition to regular dividends. These are often given when a company has excess cash or wants to reward shareholders for a specific event, such as a successful merger or acquisition.
How are dividends calculated?
The amount of dividend a shareholder receives is determined by the company’s dividend policy. Generally, companies set a fixed amount or a percentage of their earnings to be distributed as dividends.
For example, if a company has a dividend policy of paying out 50% of its earnings and it earns $1 per share, the dividend per share would be $0.50.
It’s important to note that not all companies pay dividends. Some companies may choose to reinvest their profits back into the business for growth, while others may not generate enough profits to distribute as dividends.
Benefits and considerations for investors
For investors, dividends can offer several benefits:
- Income Stream: Dividends provide investors with a regular income stream, especially for those who rely on their investments for retirement or passive income.
- Stability: Companies that pay dividends consistently are often seen as stable and financially healthy.
- Compounding: Reinvesting dividends can help accelerate the growth of an investment portfolio through compounding. By using dividend payments to purchase additional shares, investors can increase their holdings and potentially earn even more dividends in the future.
However, there are also some considerations to keep in mind:
- Risk: Dividends are not guaranteed. Companies can reduce or eliminate their dividends if they face financial difficulties or decide to allocate their profits elsewhere.
- Taxes: Dividend income is generally taxable. The tax rate depends on various factors, including the investor’s tax bracket and the type of dividend received.
- Opportunity Cost: Investing in dividend-paying stocks means potentially missing out on other investment opportunities that may offer higher growth but do not pay dividends.
Conclusion
Dividends play an important role in the world of investing. They provide investors with a regular income stream, signal financial health, and can contribute to the growth of an investment portfolio. However, it’s crucial to understand that not all companies pay dividends, and there are risks and considerations associated with dividend investing. As with any investment decision, it’s important to carefully evaluate your goals, risk tolerance, and the specific characteristics of the companies you are considering.